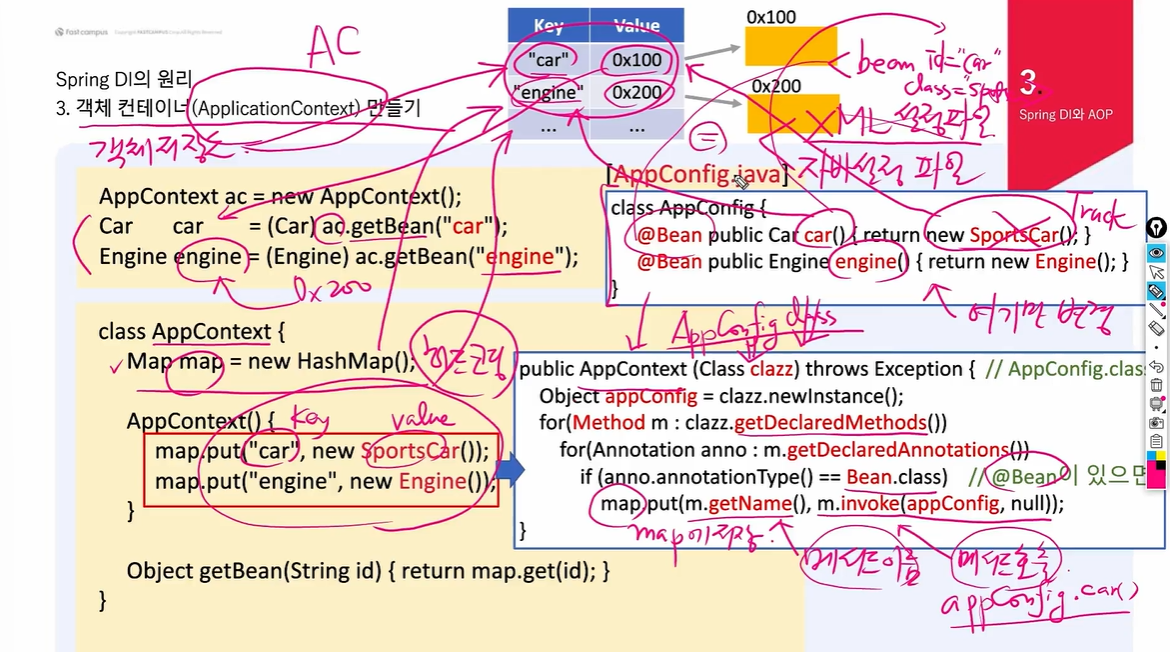
1. 객체 컨테이너(ApplicationContext) 만들기
- 객체 저장소
2. 객체 찾기 - byName, byType (Map에서 객체를 찾는 두 가지 방법)
- byName : 이름으로 찾기 -> Key
- byType : 타입으로 찾기 -> Value에서 instanceOf
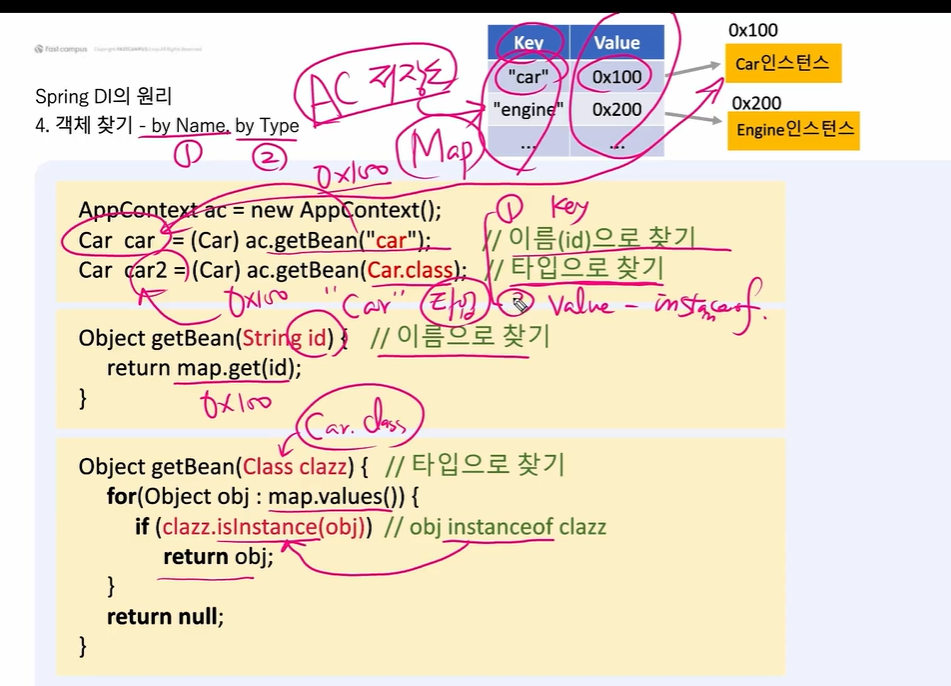
- byName으로 찾기
@Setter
@ToString
class Car{
Engine engine;
Door door;
}
class SportsCar extends Car{}
class Engine{}
class Door {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AppContext ac = new AppContext();
Car car = (Car)ac.getBean("car"); // byName
System.out.println("car = " + car);
}
}public class AppContext {
Map map = new HashMap();
AppContext(){
map.put("car", new SportsCar());
map.put("engine", new Engine());
map.put("door", new Door());
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return map.get(id);
}
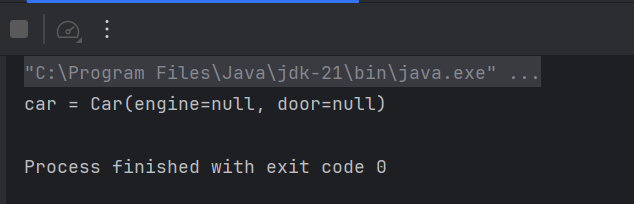
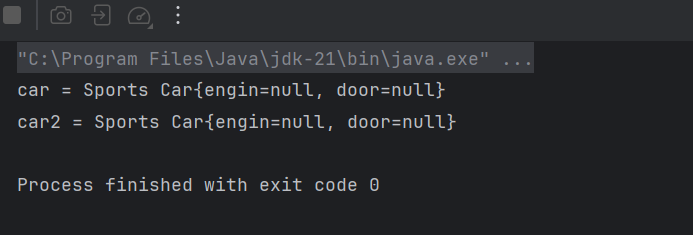
}- Key car에는 SportsCar가 들어있지만 Car가 나오는이유... SportsCar에는 ToString이 안되어있기때문
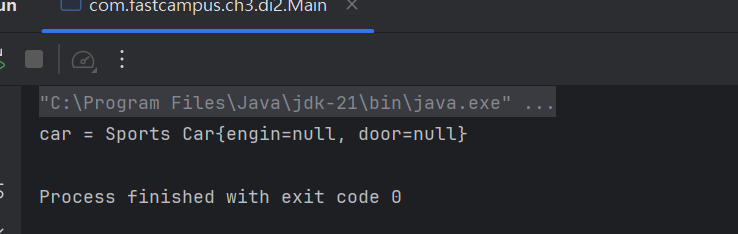
class SportsCar extends Car{
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Sports Car{" +
"engin=" + engine +
", door=" + door +
"}";
}
}- SportsCar에 toString을 오버라이딩 해주면...
- byType으로 찾기
@Setter
@ToString
class Car{
Engine engine;
Door door;
}
class SportsCar extends Car{
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Sports Car{" +
"engin=" + engine +
", door=" + door +
"}";
}
}
class Engine{}
class Door {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AppContext ac = new AppContext();
Car car = (Car)ac.getBean("car"); // byName
Car car2 = (Car)ac.getBean(Car.class); // byType
System.out.println("car = " + car);
System.out.println("car2 = " + car2);
}
}public class AppContext {
Map map = new HashMap();
AppContext(){
map.put("car", new SportsCar());
map.put("engine", new Engine());
map.put("door", new Door());
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return map.get(id);
}
public Object getBean(Class clazz){
for (Object obj : map.values()) {
if(clazz.isInstance(obj)){
return obj;
}
}
return null;
}
}
- 설정파일을 이용한 방법
public class AppContext {
Map map = new HashMap();
AppContext(){
map.put("car", new SportsCar());
map.put("engine", new Engine());
map.put("door", new Door());
}
AppContext(Class clazz) throws Exception{
Object config = clazz.newInstance();
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : methods){
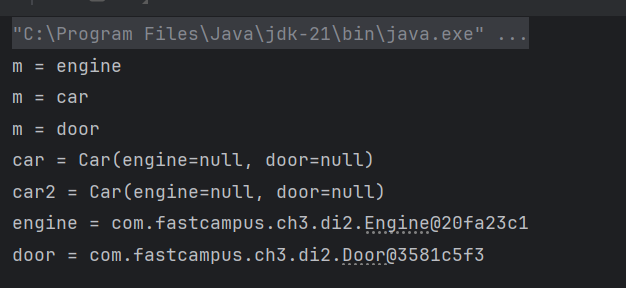
System.out.println("m = " + m.getName());
for (Annotation anno : m.getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if(anno.annotationType()== Bean.class)
map.put(m.getName(), m.invoke(config, null));
// map.put("car", config.car());
}
}
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return map.get(id);
}
public Object getBean(Class clazz){
for (Object obj : map.values()) {
if(clazz.isInstance(obj)){
return obj;
}
}
return null;
}
}- 메서드들 중 @Bean이 붙은 메서드들을 map에 저장하는 생성자
public class AppConfig {
// <bean id ="car" class="com.fastcampus.ch3.Car">
@Bean public Car car(){ // 메서드 이름이 빈의 이름
// map.put("car", new car());
Car car = new Car();
return car;
}
@Bean public Engine engine() { return new Engine(); }
@Bean public Door door() { return new Door(); }
}- 메서드 실행시 객체를 반환하는 @Bean 태그가 붙은 메서드들
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// AppContext(Class clazz) - 설정파일 자바클래스를 지정
AppContext ac = new AppContext(AppConfig.class);
Car car = (Car)ac.getBean("car"); // byName
Car car2 = (Car)ac.getBean(Car.class); // byType
Engine engine = (Engine)ac.getBean("engine");
Door door = (Door)ac.getBean(Door.class);
System.out.println("car = " + car);
System.out.println("car2 = " + car2);
System.out.println("engine = " + engine);
System.out.println("door = " + door);
}
}
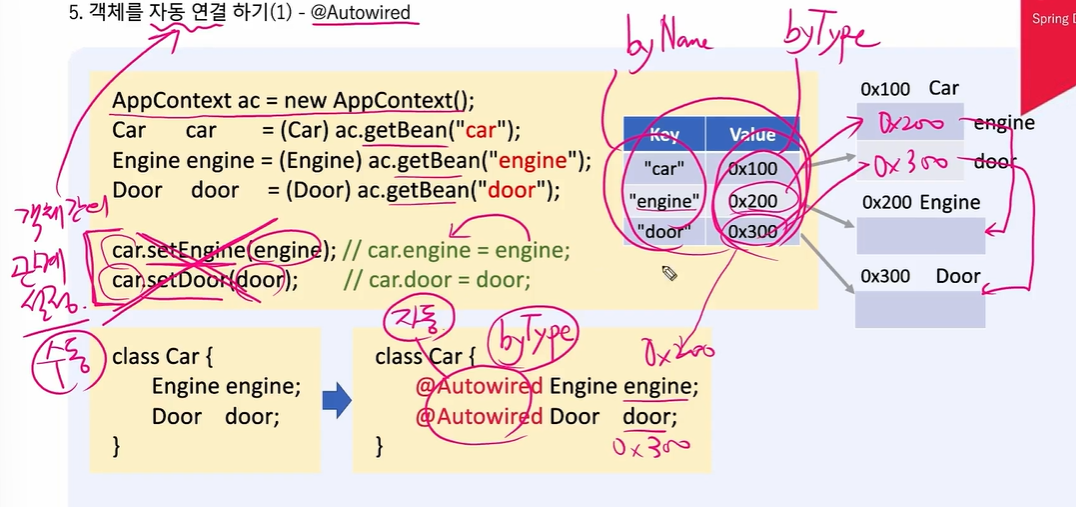
3. 객체를 자동 연결 하기 - @Autiwired
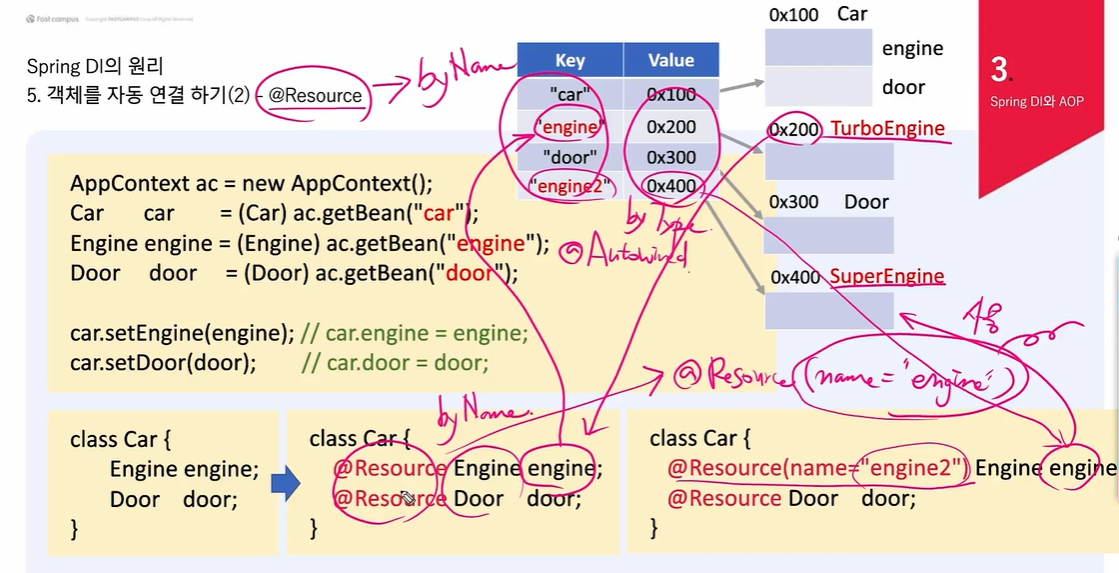
4. 객체를 자동 연결 하기 - @Resource
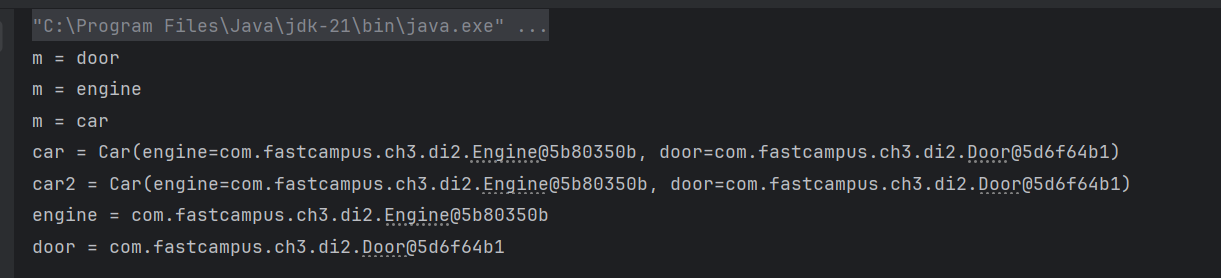
- 수동 연결
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// AppContext(Class clazz) - 설정파일 자바클래스를 지정
AppContext ac = new AppContext(AppConfig.class);
Car car = (Car)ac.getBean("car"); // byName
Car car2 = (Car)ac.getBean(Car.class); // byType
Engine engine = (Engine)ac.getBean("engine");
Door door = (Door)ac.getBean(Door.class);
// Bean들끼리의 관계를 설정 - 수동
car.setEngine(engine);
car.setDoor(door);
System.out.println("car = " + car);
System.out.println("car2 = " + car2);
System.out.println("engine = " + engine);
System.out.println("door = " + door);
}
}
- @Autowired를 이용한 자동 연결
public class AppContext {
Map map = new HashMap();
AppContext(){
map.put("car", new SportsCar());
map.put("engine", new Engine());
map.put("door", new Door());
}
AppContext(Class clazz) throws Exception{
Object config = clazz.newInstance();
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : methods){
System.out.println("m = " + m.getName());
for (Annotation anno : m.getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if(anno.annotationType()== Bean.class)
map.put(m.getName(), m.invoke(config, null));
// map.put("car", config.car());
}
}
doAutowired(); // @Autowired를 찾아서 빈(객체)간의 자동 연결처리
}
private void doAutowired() throws Exception {
for(Object bean : map.values()){
for(Field fld : bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){
if(fld.getAnnotation(Autowired.class)!=null){
fld.set(bean, getBean(fld.getType())); // car.engine = obj
}
}
}
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return map.get(id);
}
public Object getBean(Class clazz){
for (Object obj : map.values()) {
if(clazz.isInstance(obj)){
return obj;
}
}
return null;
}
}- @Autowired를 입력해주면..
@Setter
@ToString
class Car{
@Autowired Engine engine; // byType으로 자동검색해서 주입
Door door;
}
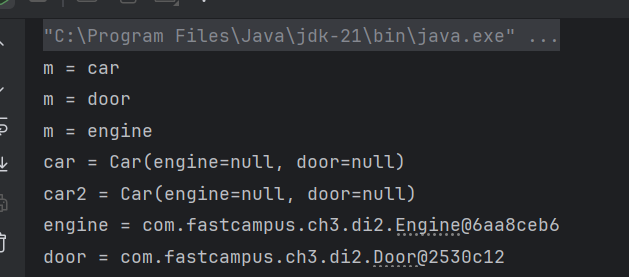
- null이었던 engine이...
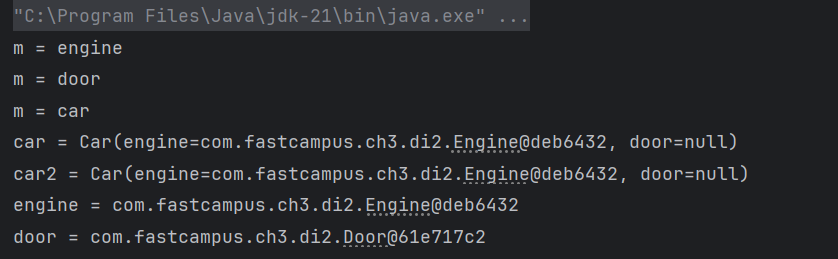
- 객체가 들어간 모습
- @Resource를 이용한 자동 주입
AppContext(Class clazz) throws Exception{
Object config = clazz.newInstance();
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : methods){
System.out.println("m = " + m.getName());
for (Annotation anno : m.getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if(anno.annotationType()== Bean.class)
map.put(m.getName(), m.invoke(config, null));
// map.put("car", config.car());
}
}
doAutowired(); // @Autowired를 찾아서 빈(객체)간의 자동 연결처리 byType
doResource(); // @Resource를 찾아서 빈ㄱ(객체)간의 자동 연결처리 byName
}
private void doResource() throws Exception{
for(Object bean : map.values()){
for(Field fld : bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){
if (fld.getAnnotation(Resource.class) != null) {
fld.set(bean, getBean(fld.getName()));
}
}
}
}- @Resource 태그를 붙여주면...
@Setter
@ToString
class Car{
@Autowired Engine engine; // byType으로 자동검색해서 주입
@Resource Door door; // byName으로 자동검색해서 주입
}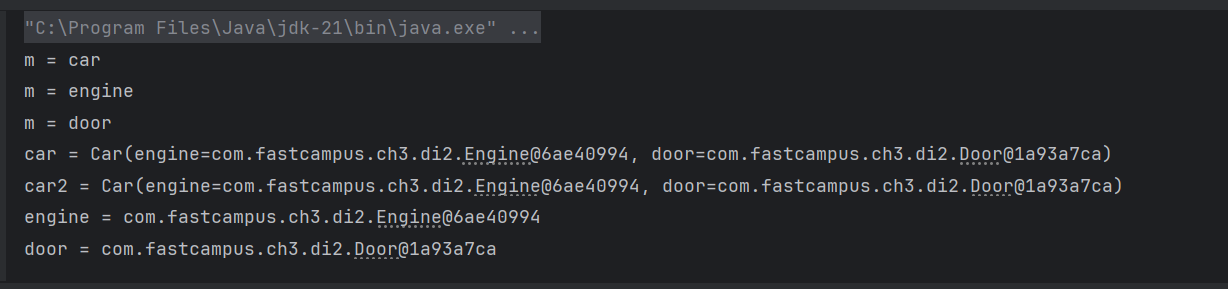
- 잘 나오는 모습..
'Spring DI, AOP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. 의존성 관리와 설정의 자동화(1) - 패스트캠퍼스 백엔드 부트캠프 3기 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
|---|---|
| 5. Spring 애너테이션 - 패스트캠퍼스 백엔드 부트캠프 3기 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
| 4. Bean과 ApplicationContext - 패스트캠퍼스 백엔드 부트캠프 3기 (2) | 2025.02.24 |
| 2. Java Reflection API - 패스트캠퍼스 백엔드 부트캠프 3기 (2) | 2025.02.21 |
| 1. Spring DI의 원리(1) - 패스트캠퍼스 백엔드 부트캠프 3기 (0) | 2025.02.20 |